
Polyphenols From Olive Leaves – Shelf Life Improvisation
Polyphenols are widely recognised for their health benefits, and polyphenol-rich olive oil, which is a staple of the Mediterranean diet, has been linked to improved health. Olive leaves, on the other hand, have been discovered as a polyphenol-rich alternate source in the last decade. This is particularly interesting in the context of the growing interest in functional foods, as well as in terms of the management of biological waste, including olive leaves that are left over from the production of olive oil. Previous research has found that olive leaves have a high phenolic content, which explains their previously reported antibacterial, antimicrobial, and antiviral properties.
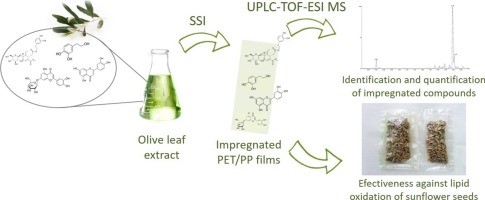
Fig.1. Characterization of Olive Leaf Extract Polyphenols (ScienceDirect.com)
Many recent studies have shown that commercially available polyphenols and polyphenol-rich extracts inhibit lipid peroxidation in meat and meat products and preserve meat colour better than/or as well as the synthetic antioxidants butyl hydroxy anisole (BHA), butylhydroxytoluene (BHT), tert-butylhydroquinone (TBHQ), and propyl gallate (PG), which have been suspected to have negative effects on human health.
Consumers, on the other hand, have recently asked that these chemicals be replaced with natural molecules that have beneficial effects. Commercially available polyphenols and plant extracts rich in polyphenols may be effective for protecting meat/meat products from oxidative degradation, bacterial spoilage, and pathogen growth due to their antioxidant and antibacterial capabilities.





