
Optimizing Your Budget: Smart Food Procurement Strategies
Cost-Effective Food Ingredient Procurement Strategies
Last Updated: 01/05/2024
Introduction
Food expenditures can be significantly decreased by doing a food procurement. The procurement must therefore take into account the requirements of the whole company in order to adhere to the agreement. Inadequate planning in the procurement process increases the likelihood of purchases made outside of the contract, which raises expenses. The COVID-19 outbreak has caused numerous disruptions to nearly every industry. Therefore, a study on food ingredient procurement techniques has been conducted to offer affordable approaches to aid in decision-making. 2
Developing a Strong Supply Foundation
The prices of commodities have sharply decreased over the last two years. However, in order to take advantage of these drops as soon as possible, businesses must have the tools necessary to recognize and quantify savings opportunities as well as a flexible procurement procedure to seize them. A growing number of companies in the food business are using methodologies for clean-sheet cost modelling. A buyer can develop a thorough understanding of the cost drivers of both current and potential suppliers by utilizing clean-sheet procedures. With the use of this knowledge, they are better able to construct successful requests for quotations (RFQs), identify the best negotiating and go-to-market tactics, and optimize variables like the award duration and the extent to which pricing will be indexed to underlying commodity costs. 1
Augmenting Specifications
Businesses can better determine which elements of their goods are most important to customers by using design-to-value strategies. Careful evaluations of consumer preferences and tastes can frequently open up potential for major cost savings for food players by allowing specifications to be changed or lower-priced ingredients to be substituted. Value-added procedures and components can potentially raise the value of the product and boost sales. For example, a large food manufacturer was able to mimic the taste and flavour of eggs with a combination of vegetarian components. The food’s colour, texture, or flavour were unaffected by the new formulation, which also had the added benefit of making the product kosher and lowering total costs.
Companies can lessen their exposure to the volatility of commodities prices by using a flexible approach. One cheese manufacturer, for instance, created multiple formulations for each product using a flexible formulation method. One of the most important components of this strategy was for the corporation to modify its systems so that it could switch between recipes; this allowed it to adjust the recipe based on the relative cost and availability of ingredients or in response to the preferences of various customer segments. Due to this flexibility, businesses have also been able to reduce the negative effects of currency fluctuations by swiftly and effectively modifying their supply chains to obtain from the nation with the lowest costs at any given time.
Key Principles in Purchasing
Generally, there are nine principles with regards to effective purchasing:
- Supply Continuity: This is crucial to reducing or completely eliminating interruptions to the process of producing food.
- Smallest investment in stock: The amount to be stored must be carefully evaluated while making a purchase.
- Stocks Security: The needs of current usage must be properly balanced with forward buying. Security for stocks includes not just keeping them safe from robbery or pilfering, but also avoiding spoiling or quality degradation while they are being stored.
- Consistency in Quality: The goal of buying is to acquire products that best meet manufacturing needs for final usage but also ranking lowest in terms of absolute quality when it comes to brands, grades, or standard quality. Perishable goods should be brought straight into the kitchen in order to prepare delicious meals.
- Procurement at less cost: When it comes to purchasing food supplies, the best course of action is to go for the lowest total cost rather than the lowest starting cost. This is typically accomplished by buying large packages directly from manufacturers and relying on a single supplier that understands the numbers and quality needed over the long run.
- Eliminating Wastage: avoiding waste and redundancies to reduce food waste and duplication of procurement time and effort, which might arise from unforeseen menu changes or alterations in production policies, communication between the purchasing, production, and user departments is essential.
- Maintenance of competitive position: Purchasing managers must be well-versed in both the competitive landscape and the purchasing practices of companies that provide comparable products and services to their clientele. This calls for a high level of executive judgment and experience in order to predict future shifts in client preferences. By highlighting costs, quality, and pricing that the market will accept, a buying manager who can notify the production and service divisions of these changes ahead of time may keep their competitive edge.
- Establishing relationship with supplier: Establishing a value-based reputation through strong ethical standards that are mirrored in a supplier’s interactions with employees, purchasing managers, and the business at large is crucial. A supplier experiences a feeling of allegiance to the company and perceives honesty in business dealings rather than being taken advantage of through bribery and corruption.
- Harmonious environment: Mutual respect and understanding are the outcomes of relationships that grow and foster harmony and collaboration among all members of an institution, both inside and outside of it. 3
Conclusion:
In process of determining the best strategy for cost-effective sourcing of food raw materials, it would be ideal if food manufacturers can answer the below questions:
- Is your company really aware of how its supply chains are structured, from farm to factory, and what the fundamental cost drivers are?
- Are you making every effort to take advantage of the current cheap commodity prices?
- Are you prepared to react to abrupt or protracted shifts in the dynamics of the supply-market, such as increases in the price of commodities or energy in the future?
How Guires FRL CDMO Solves the Problem:
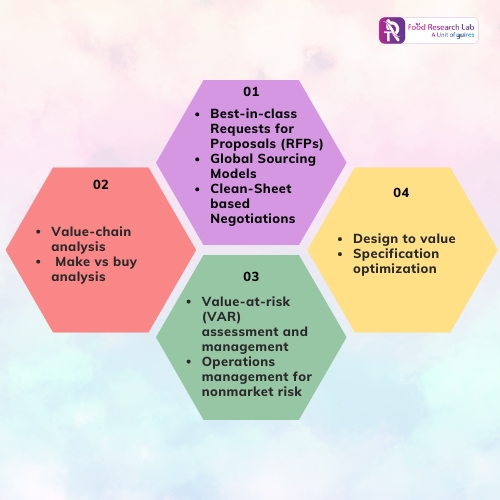
With the use of tried-and-true, proprietary databases and techniques, Guires Food Research Lab CDMO aims to provide food businesses with strong support in maximizing the overall value of their raw material specifications and production processes.
Reference:
- https://ebooks.inflibnet.ac.in/hsp06/chapter/procurement-methods-for-foods/#:~:text=Compare%20purchasing%20by%20retail%2C%20wholesale,group%20of%20commodities%20if%20possible.
- https://publication.sipmm.edu.sg/crucial-factors-effective-food-procurement/
- https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/consumer-packaged-goods/our-insights/recipe-for-success-for-sourcing-in-the-food-industry





