Plant protein-based packaging
INTRODUCTION
- Plant-based proteins have captured the interest of the worldwide packaging industry in the recent decade due to their biodegradability, sustainability, environmental, and health benefits.
- Natural biopolymers such as polysaccharides, lipids, and proteins are being used as the foundation for constructing biodegradable packaging (bio-packaging).
- Proteins have attracted much interest among biopolymer materials because of their ability to form translucent films that can operate as good oxygen barriers and give certain mechanical qualities.
- Protein-based edible films offer greater mechanical properties than other sources. Treatments and agents are typically used during protein film synthesis to improve the characteristics of protein films.
- Plant-protein sources have sparked considerable interest among diverse naturally produced biopolymers due to their outstanding film formability, high mechanical properties, cohesive/adhesive capabilities, low edibility, and rapid biodegradability.
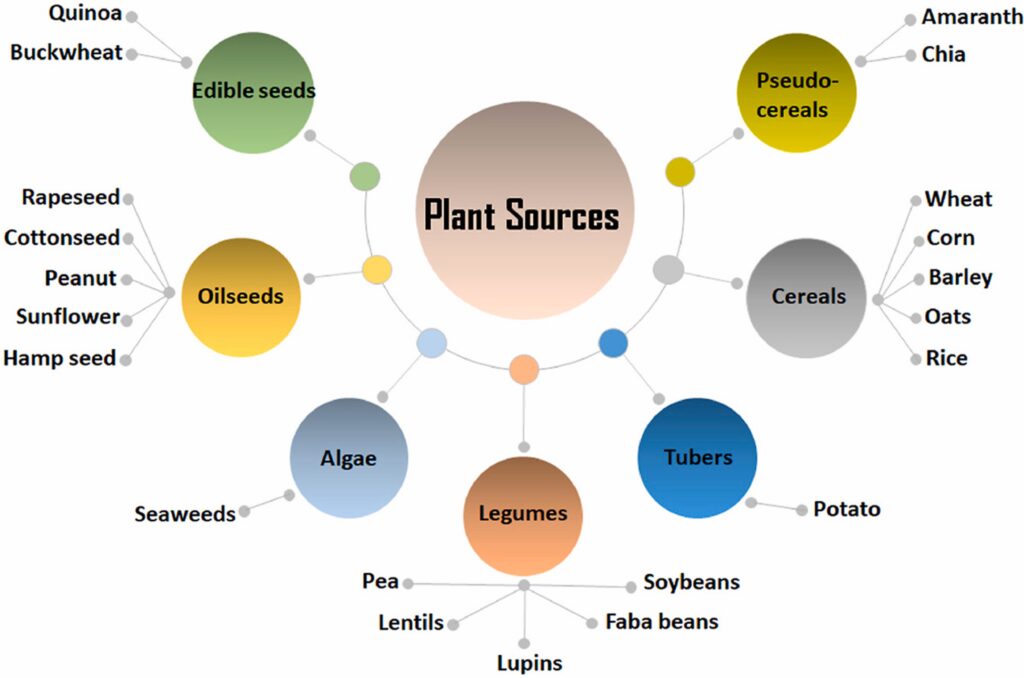
- Soy, wheat, corn, pea, barley, quinoa, and mung bean are the most common plant protein sources, and they include hydrophobic and antioxidant proteins that form an adhesive film. [1]
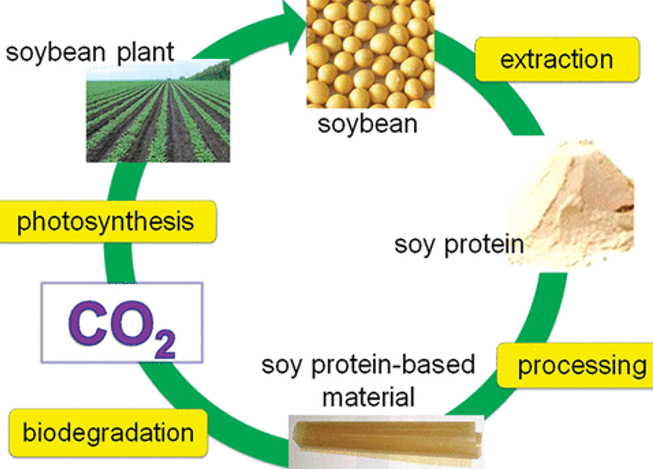
Fig.1 Process flow for Soy protein Based Packaging Material
Hazards caused by conventional packaging:
- Plastic materials are widely used, and despite the numerous benefits and advantages they bring to humans and society, their negative impacts are notable. Ingestion of microplastics and their byproducts (BPA and DEHP) is hazardous. It may cause health issues. Furthermore, the material disintegration period is lengthy, and as a result, plastic waste accumulates in the environment, posing a severe threat to animals and plants.
- The packaging segment is the highest and fastest-growing user of fossil-fuel-derived synthetic polymers. Plastics used in food packaging generate the majority of plastic waste contaminating the environment. Conventional plastics are not biodegradable and take a long time to degrade. They are also resistant to ageing, degrade into smaller debris, and accumulate in the environment.
- Several chemicals used in the manufacture of plastics, unbounded monomers, additives, and their breakdown products may be released into the environment during the lifespan of a plastic product, which may have dangerous effects for biological life and the environment. [4]
Applications
- Proteins’ excellent film-forming characteristics have elevated protein-based films to the forefront of food packaging material development.
- Each type of food has distinct storage requirements, which necessitates packaging materials that fulfill specified storage conditions for certain foods.
- Protein-based biopolymer materials can be modified to meet the requirements of various food packaging materials.
- Proteins’ nutrition and biodegradability make them one of the greatest food packaging materials.
- Furthermore, the choice of food packaging materials must take environmental elements into account, such as relative humidity, temperature, and light intensity, to which the foods are exposed during distribution and storage.
- Protein-based films and coatings were widely employed in fruit and vegetable preservation. [3]
- The application of zein coatings to tomatoes delays color change, softening, and weight loss without producing ethanol.
- Due to its complexity and changes in characteristics, cheese is one of the most studied and demanding dairy products.
- Because of its biochemically and physiologically active character, edible films and coatings are commonly employed to extend the shelf life of various cheeses.
- The most critical issue in cured meat preservation is preventing degradation caused by discoloration.
- For enhancing quality and safety, environmentally friendly plant-based protein packaging is extensively utilized, and several packaging technologies, such as vacuum, aseptic, modified atmosphere, intelligent, active, and so on, have been created. [3]
Advantages
- It requires less carbon to create, decreases trash sent to landfills, and emits no pollutants as it degrades.
- The commercial benefits are sometimes ignored, but they are as important.
- Plant-based products are manufactured from materials that are renewable, low-carbon, or recycled.
- Plant-based packaging is biodegradable and does not add to landfill waste.
- Plant-based materials are both sustainable and environmentally friendly.
- There are a variety of plant-based materials suitable for different kinds of food. [2]
Disadvantages
- There are some drawbacks as well. Plant-based bags may be less strong and durable than standard plastic bags.
- Furthermore, depending on the manufacturing method, these bags may necessitate additional resources and energy [2].





