
Formulation of Protein-Based Healthy Cereals: FRL Methodology
Importance of Breakfast and Role of Breakfast Cereals Essential Part of Breakfast and Ultimate Purpose of Breakfast Cereals
Breakfast is one such vitally important meals for the human-beings. A beneficial attribute of breakfast is tremendously important for growing people like children and adolescents, to bolster pertinent physical fitness. Time is not a sole concern in consuming breakfast, at least a consumption of 50 kcal energy is imperative in the course of time. Beginning the day with cereals inspired health food choices for the entire day. As devouring cereals in breakfast is the premier meal of the day in the morning, it was bound together with augmented consumption of carbohydrates and fiber, and lessened diet of fat all day long. Consuming whole cereals was also associated with enhanced utilization of generous portion of micronutrients that consequently contribute to best grade breakfast. Therefore, breakfast cereals deliver a endless options for meeting everyday compliments in such a way that diet of whole grain can be appropriated by the individuals of any age groups.
Exploitation of Bajra or Pearl Millet in the Development of Breakfast Cereals
The objective of this client’s project was to formulate a nutrient rich Ready to Eat (RTE) breakfast cereal (BC) by utilizing popped pearl millet (bajra). Pearl millet is nutritiously superlative to primary cereals particularly to rice and wheat, considering that it is a excellent source of carbohydrates, protein, and dietary fiber and micronutrients. Pearl millet is piled with vitamins, potassium, phosphorous, magnesium, zinc, copper and manganese. The phytochemicals like tannins and phytates serves as antioxidant properties. It has poor glycaemic index and also exhibits a finite amount of flavonoids that are gluten free. Pearl millet has significant amount of calcium , iron, zinc, lipdis, and amino acids such as lysine, tryptophan, threonine and fatty acids namely omega-9, omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids.
A ready-to-eat snack mix embodied with minor cereals was identified to be exorbitant in proteins and minerals and advantageous for every age groups. A ready-to-eat breakfast cereal (BC) attributed with popped pearl millet was purposed and estimated for its nutritional profile and appropriateness, taking into consideration the nutritional facts of pearl millet.
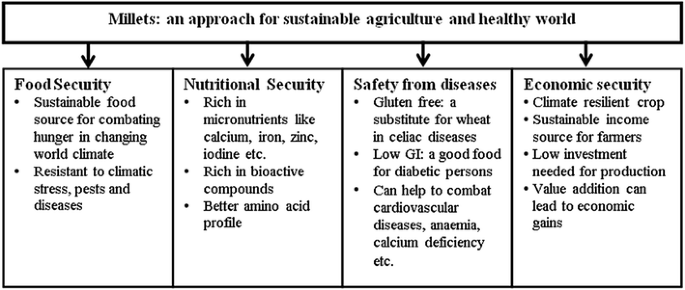
Fig.1. An Explication to Nutritional Challenges (BioMed Central.com)
Process and Nutritional Analysis of Product Formulation
Pearl millets are traditionally pulverised to whole meal and used in unleavened pancakes, dumplings, thin porridges, and other unleavened foods; however, processing and diversification of this millet for other food uses and value-added goods has not been fully utilized. This grain’s processing and product diversification has recently gotten a lot of attention. When phytic acid, a prominent anti-nutritional component in pearl millet, was measured in the popped pearl millet, it was found to be significantly lower. As a result, the nutritional popped grain was discovered to be an excellent snack. The popped pearl millet, like popped rice or maize, was discovered to have market potential, particularly in terms of nutritional benefits.
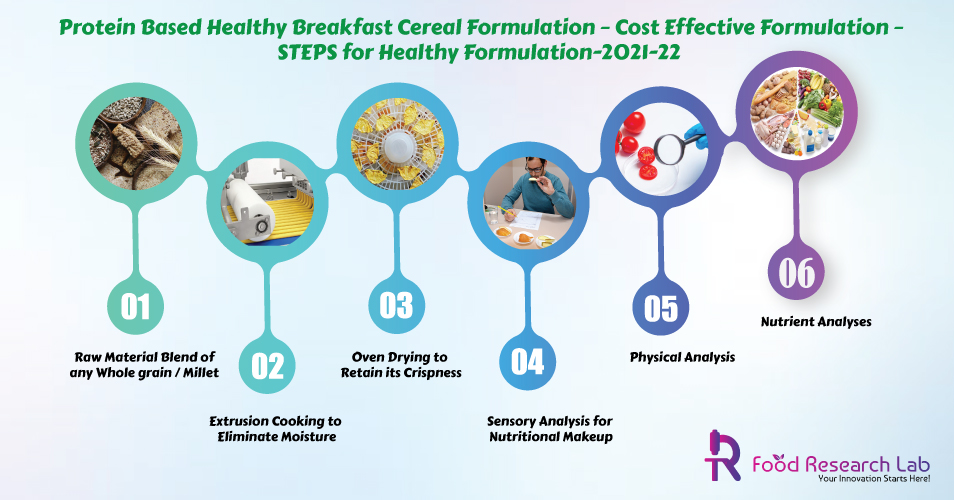
The grains were washed to remove dust and other non-essential impurities before being stored in plastic containers at room temperature. Along with popped pearl millet, other cereals and pseudo cereals such as popped amaranth, puffed wheat, flax seeds, sunflower seeds, raisins, honey, sugar, oil, and water were mixed, baked, and cooled to make the breakfast cereal. It was followed by popping, puffing, roasting, RTE-BC preparation, sensory, physical, and nutrition analyses.
Sensory Analysis: A sensory evaluation of morning cereal made with various dry ingredient formulations was conducted in order to obtain a product with a high acceptability. On the basis of sensory evaluation, the most popular morning cereal was investigated further for physical properties and nutritional makeup.
Physical Analysis: Bowl life and bulk density analyses were included in the physical analysis. The amount of time that the cereal may retain its crispness after being soaked in milk was used to determine bowl life. Breakfast cereal samples were soaked in 30 cc of milk in ten separate beakers. Every 2 minutes, the breakfast cereal was taken from the milk and carefully pat dried to eliminate any excess milk without breaking the cereal. The percentage of weight gain was recorded and reported. To assess bulk density, the volume of 100 g of product was measured using a measuring cylinder after tapping it on a wooden plank until no noticeable drop in volume was observed. The apparent density was computed using the weight and volume.
Nutrient Composition: The contents of moisture, crude protein, ash, crude fibre, and fat were determined. By deducting the total of moisture, protein, fat, and ash from 100, carbohydrate was calculated. The nutritious adequacy of the popped pearl millet breakfast cereal was determined by calculating the percent RDA for a serving size of 40 g of cereal with 120 ml of skimmed milk. The figures are based on 100 g of dry materials.
Statistical Analysis: Three separate trials were used in the tests, and the results are reported as mean standard deviation (SD). To discriminate between the means of distinct samples, Duncan’s Multiple Range Test was utilised. The produced morning cereal was comparable to market samples in terms of calorie, fat, and carbohydrate content. In comparison to the market samples, the proposed breakfast cereals delivered a higher amount of protein. Proteins, dietary fibres, folic acid, and minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and iron were abundant in the proposed RTE-breakfast cereal. RTE-BC contains a good level of total dietary fibre, according to this project. When compared to market samples such as Kellogg’s, Baggary, and others, the produced morning cereal was comparable in terms of protein, fat, calories, and carbohydrate, but somewhat greater in terms of folate and other important micronutrients. As a result, this millet’s nutritional superiority is an extra benefit that will help it gain market share and demand in the food business.
Summary
The manufacturing method is cost-effective and can be quickly scaled up from home to industrial scale using locally available underused grains. Because the bran is maintained in the finished product, using whole grain has nutritional benefits. It’s also cost-effective because no by-products are created during the process. Overall acceptability was likewise high according to sensory analysis. This technique may be used to prepare pearl millet-based breakfast cereals for commercial purposes, and it can be scaled up by interested entrepreneurs.

References
- Kumari, R. I. T. U., Singh, K. A. R. U. N. A., Singh, R., Bhatia, N., & Nain, M. S. (2019). Development of healthy ready-to-eat (RTE) breakfast cereal from popped pearl millet. Indian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 89(5), 877-881.
- Kumari, R., & Nain, K. S. M. S. Nutritional evaluation and storage stability of popped pearl millet bar.
- Bansal, T., & Kawatra, A. Millets-Health Benefits and Processing Methods.
- Karthiayani, A. (2021). Thermal Processing of Traditional Fermented Pearl Millet Porridge in Ready-to-Eat (RTE) Form. The Indian Journal of Nutrition and Dietetics, 58(1), 79-91.





