
Recent practices in Green Technologies in Food Production and Processing
Introduction
The food consumed every day must be processed so that they are fit for consumption. Various processing techniques are implemented to develop food product , like cooking, boiling, filtering and frying. These techniques have been implemented for a long time, and are therefore called conventional food processing techniques. However, some shortcomings occur in this process, like low efficiency and, hence, more time and energy consumption. In addition, the loss of nutrients in food can indirectly affect consumers’ immune systems. These drawbacks have led to food development innovations that follow sustainable practices, from processing to pasteurisation and extraction.
The following points discuss greener innovations occurring in the food industries:
1.Instant controlled pressure drop technology
Also called ‘Détente Instantanée Contrôlée‘ (DIC) in French, the Instant controlled pressure drop technology is considered to be a High-Temperature, High-Pressure, Short Time (HTST) type of thermal process. It has many applications in the food industry, such as decontamination, preservation and extraction. DIC decreased processing time in the experimental models, and the sudden pressure drop ensures a higher food quality by preventing thermal deterioration.
2.Microwave extraction
Microwave has numerous uses in food formulation, like drying, baking, pasteurisation and sterilisation. In 1986, Ganzler and Lane published the first description of the use of microwave energy for extracting food components. There has been an increasing interest in more sustainable extraction processes recently. Approaches such as Solvent-Free Microwave Hydrodistillation (SFMH) and Microwave Hydrodiffusion and Gravity (MHG) have been developed. SFMH has the advantage of far lower carbon dioxide emissions in the extraction of essential oils (200g CO2 using the SFMH method compared to 3600g CO2 while using solvents). MHG does not require the steps of evaporation and distillation processes, which are the most energy-consuming [1].
3.Enzymes
Enzymes have recently been gaining a lot of attention in food processing that can help decrease the environmental impact. Enzymes have many advantages high activity at low temperatures, specificity, and ease of inactivation. The specificity of enzymes results in the production of consistent products. A range of food items can be made from harvested produce thanks to the action of enzymes in foods, which has advantages such as extending shelf life of food and improving sensory properties, functioning, and yield. In addition, enzymes are more environmentally friendly since they incorporate milder treatments. Amylase, pectinase, bromelain, trypsin and glucose oxidase are some enzymes used in food processing [2]. Studies have also shown that enzymes have a potential for developing food flavour [3].
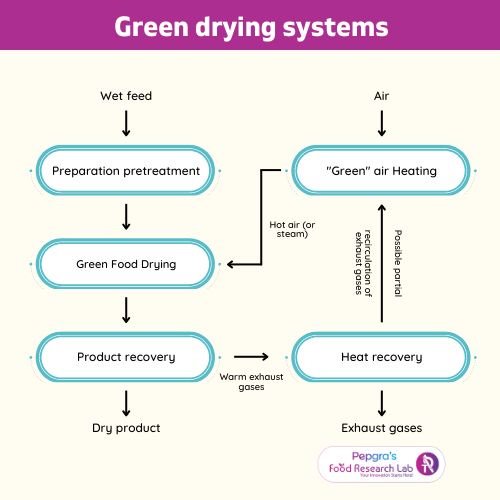
4.Drying techniques
Drying is one of the most energy-intensive processes in food product development. Innovations in reducing energy consumption in drying include using alternative forms of energy like solar energy [2][4]. Solar energy can also be exploited for cooking and pasteurization [4].
Green drying installation schemes have been introduced wherein the heat is collected from exhaust fumes and circulated. After heat recovery, exhaust gases might undergo additional cleaning to eliminate greenhouse gases.
5.Recycle and reuse water
A substantial amount of water is used in food product development , from washing the raw material to cooling the finished product. According to a study by Alkaya and Demirar, recycling and reusing water decreased the environmental impact and the total cost required for beverage formulation in the soft drink industry[5]. This practice can be implemented by the food industry as well.
6.Green Packaging
The last step in food manufacturing is packaging. Packaging is essential as it determines the overall quality of food. Packaging has other functions, such as convenient sizing of food and serving as a channel of communication with the consumer. Some considerations for sustainable food packaging include maintaining necessary functionality, minimising material use, increasing recycled content and using recyclable materials, and avoiding potentially harmful components [2].
Conclusion
Consumers have become more environmentally conscious and prefer using products manufactured by companies that consider the environment. Greener food processing has more advantages than being sustainable- they preserve the nutritional value of food and improve the overall quality. There is a huge opportunity for the food industries to meet the consumers’ new demand by being more responsible towards the environment.
How the Food Research Lab can help
The Food Research Lab has a team of experts with great enthusiasm for innovative ways of formulating food . In addition, it conducts industry and market research that helps the client set itself apart from their competitors. The team also assists in the development of packaging that helps the food stay fresh for a longer duration.





